You can also visit Online Git Tutorial section to learn about Git command line tutorials and examples.
Step 1 – Prerequisites
Use the following commands to install required dependencies to begin Gitlab installation. Now install some other required packages to complete the installation process.
Step 2 – Install Gitlab on Ubuntu
Now, enable the Gitlab Debian package repository on your system. Execute below command on your system, this will add a file /etc/apt/sources.list.d/gitlab_gitlab-ce.list in your system. After enabling apt repository, run following command to install Gitlab community edition. The above command will install all the required applications including Nginx web server to run Gitlab on your system.
Step 3 – Enable Let’s Encrypt SSL
Gitlab provides option to confiugre Let’s encrypt SSL certificate to run over secure HTTP protocol. You must have point a domain to the server’s IP. For example, I have done the following entries to our dns server. Then edit the configuration file
Step 4 – Configure Gitlab Server
Next, configure Gitlab server using the following command. This will make all the installations and required changes in order to run Gitlab community edition on Ubuntu system. The configuration process will take time to complete setup.
Step 5 – Adjust Firewall
You need to open ports in firewall to access on network. The below commands will allow http and https service in firewalld and make them permanent Next, run the following command to implement the changes:
Step 6 – Gitlab Dashboard Access
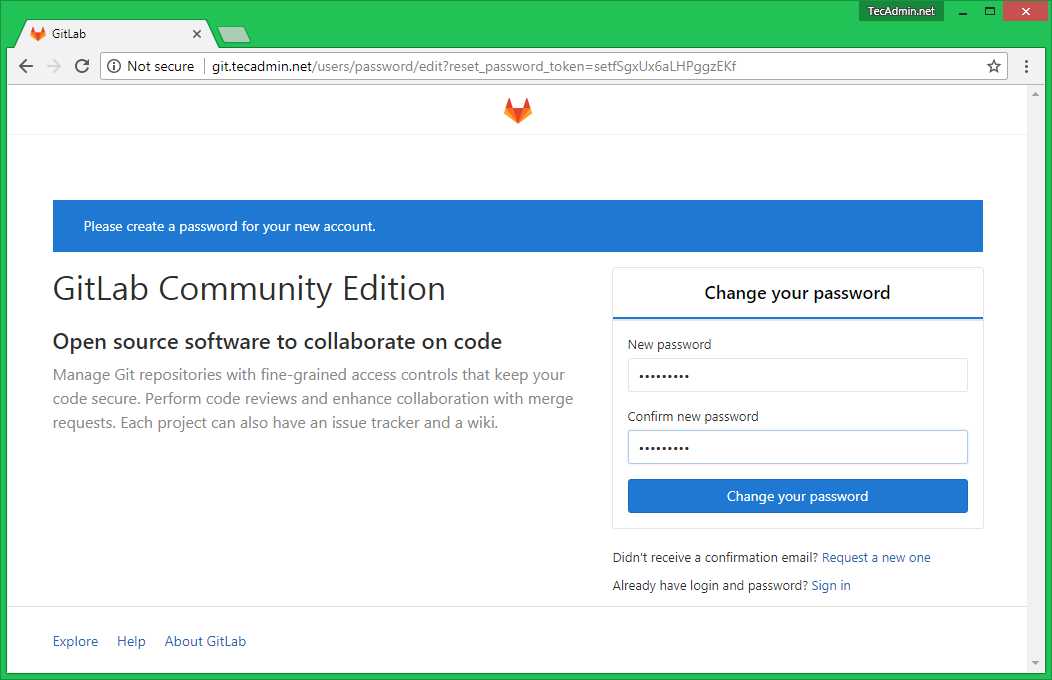
Access your server using the domain name or IP address on standard HTTP port 80. You will get the password change screen for root user for the first time as below. Update the new secure password for the root user.
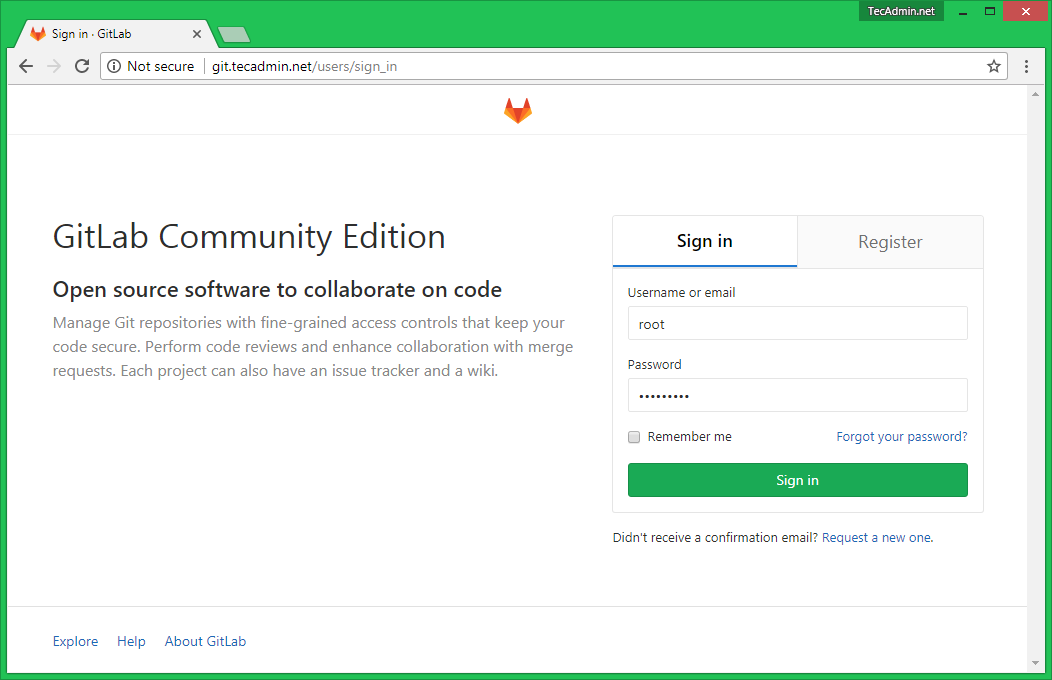
After successfully changed the password navigate to the login screen and log in with user “root” and the specified password.
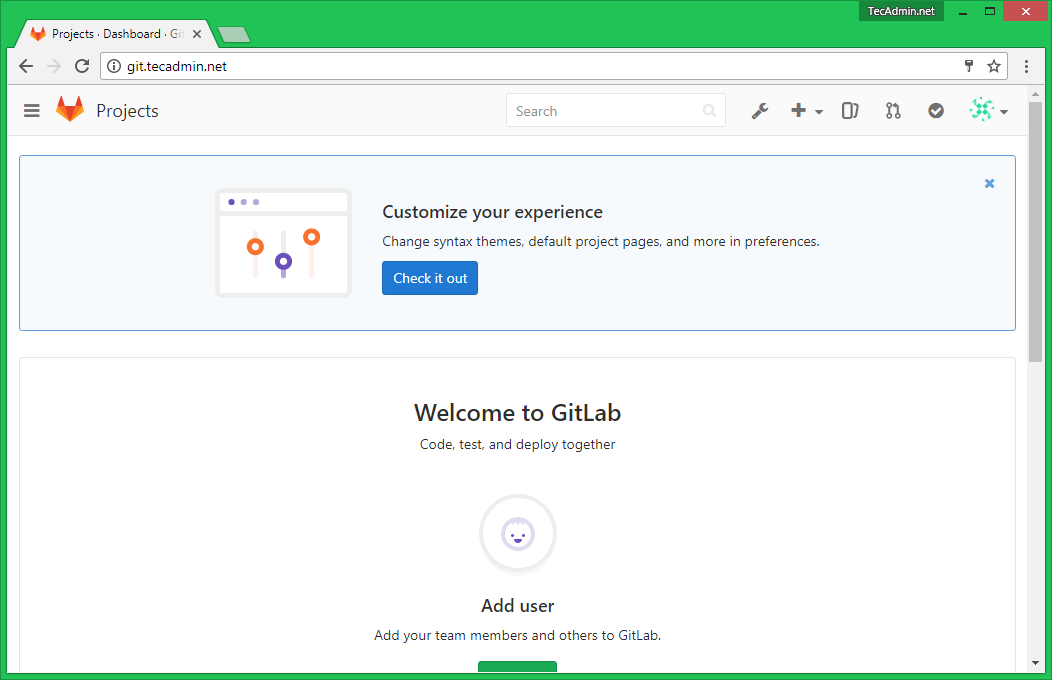
After login, you will get the dashboard access to your Gitlab server. Here you can start with the creation of users and new git repositories.
Now visit our Git Tutorial to learn more about uses of Git repositories with command line helps and examples.
Step 7 – Schedule Gitlab Data Backup
Use the following command to create the complete backup of Gitlab data. The default backup location will be /var/opt/gitlab/backups. You can change this setting in /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb file. You can also add the same command scheduler to backup data nightly. Add the below cron to the system crontab.
Conclusion
You have successfully installed and configured Gitlab community edition on your Ubuntu system.